- Development Env.
- post date : 2019. 09. 23
- OS : macOS Majave 64bit
- Java version : JDK 1.8.0 J_220 JRE8
- Eclipse : 2019-06 (4.12.0)
Java UI
AWT(Abstract Window Toolkit)
- 운영체제의 GUI를 사용한다.
- 운영체제에 따라 UI모양이 서로 달라서 다 깨진다.
- UI 종류로 제한적이었다.
Swing
- 모든 운영체제 상에서 동일한 UI를 갖도록 자체적인 지원한다.
- 사용자는 애니메이션 추가된 시각적 운영 체제의 네이티브 UI를 더 선호하게 되었다.
- 네이티브 UI로 보여지도록 자신의 UI 재정비하다보니 퍼포먼스를 많이 잡아먹게 되었다.
- 실행 성능이 느려지고, 메모리를 더 많이 사용하게 되었다. -> 시스템이 좋아진 것으로 보완이 되었다.
- Swing보다 운영체제 GUI가 더 향상되었다.
무엇보다!! 위의 두가지는 디자이너와 협업이 되지 않는다.
JavaFX
- 가볍고 풍부한 UI를 제공한다.
- 시스템의 성능을 향상시킨다. (임베디드 UI에도 도입할 만큼!)
- 소형시스템에서 JavaFX 도입가능하다.
- 디자이너와 개발자가 협업이 가능하다.
설치
[박스여우님의 설치 포스팅 링크] https://boxfoxs.tistory.com/307
JavaFX 구성요소 및 생명주기
| 레이아웃 | 외관 및 스타일 | 리소스 |
|---|---|---|
| 자바 코드 파일 또는 FXML |
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
public class AppMain extends Application{
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" : "+"main go!");
launch(args);
System.out.println("end");
}
/*필드를 초기화*/
public AppMain() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" : "+"constructor go!");
}
@Override /**/
public void init() throws Exception {
super.init();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" : "+"init call" );
}
@Override
public void start(Stage primaryStage) throws Exception {
primaryStage.show();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" : "+"start call");
}
@Override
public void stop() throws Exception {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" : "+"stop call" );
}
}
main : main go!
JavaFX Application Thread : constructor go!
JavaFX-Launcher : init call
JavaFX Application Thread : start call
JavaFX Application Thread : stop call
end
- JRE이 포함하고, 어플리케이션 상속을 받고, 메인에서 런처를 부르면 두개의 스래드를 만든다.
- 자바 스레드 / 런처 스레드
- 자바 스레드
- 런치 포함한 생성자
- 런처 스레드
- 아이 나이트
- 자바 스레드
- start를 실행하고, 매개변수의 스테이지를 실행
- 스테이지에는 씬 - 루트컨테이너 (8가지 안에 컨트롤러를 넣을 수 있다.)
- SetONAction 으로 이벤트 등록
- 창을 닫으면 stop을 실행
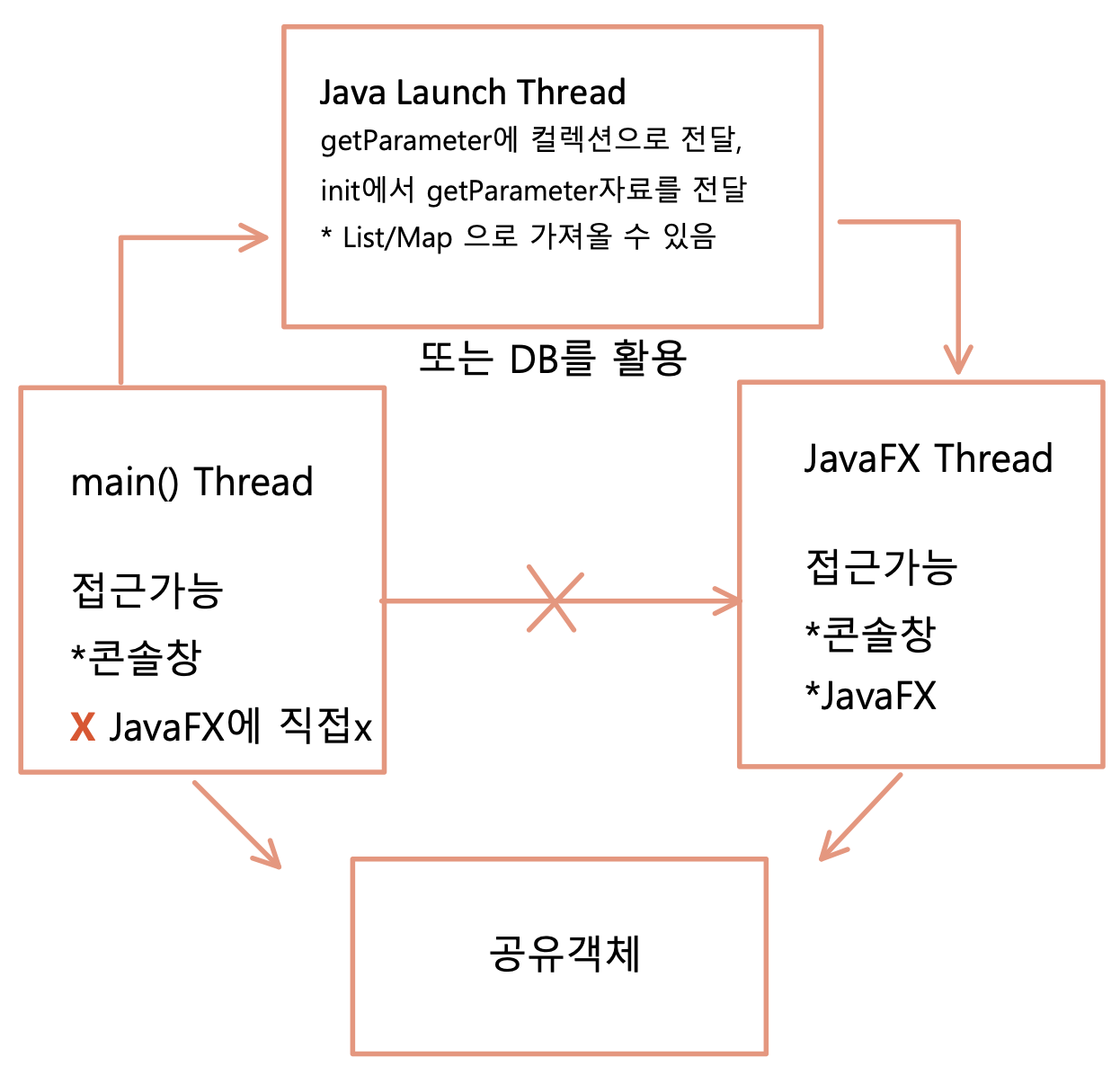
main Thread가 JavaFX로 직접 데이터를 줄 수 없기 때문에 JavaFX Launch를 통해 데이터를 전달 할 수있다. 다른 방법으로는 데이터 베이스를 이용할 수 도 있지만 여기서는 다루지 않겠다. Parameter 객체에 저장된 데이터는 컬랙션 프레임워크의 List와 Map으로 가져올 수 있다. Run Configurations -> Arguments 에서 Program arguments로 값을 주어 테스트 해 보았다.
 Format:
Format:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
public class AppMain extends Application{
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" : "+"main go!");
launch(args);
System.out.println("end");
}
public AppMain() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" : "+"constructor go!");
}
@Override
public void init() throws Exception {
super.init();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" : "+"init call" );
/*Parameter 객체에 저장된 데이터를 가지고 온다.*/
Parameters ps = getParameters();
/*List로 가지고 온 경우*/
List<String> list = ps.getRaw();
for(String value : list) {
System.out.println(value);
}
/*Map로 가지고 온 경우*/
Map<String, String> map = ps.getNamed();
Set<Entry<String, String>> set = map.entrySet();
for(Entry<String, String> entry : set) {
String key = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println("Key : "+key+" Value : "+value);
}
}
@Override
public void start(Stage primaryStage) throws Exception {
primaryStage.show();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" : "+"start call");
}
@Override
public void stop() throws Exception {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" : "+"stop call" );
}
}
main : main go!
JavaFX Application Thread : constructor go!
JavaFX-Launcher : init call
--IP=192.168.0.210
--port=2000
Key : port Value : 2000
Key : IP Value : 192.168.0.210
JavaFX Application Thread : start call
JavaFX Application Thread : stop call
end
이벤트 처리 방법
- 람다식
- 임시객체
- 함수
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
/*람다*/
buttonOK.setOnAction((event)-> {
if(fontValue) {
label.setText("HELLO");
label.setFont(new Font(30));
}
else {
label.setText("Hello, JavaFX");
label.setFont(new Font(fontSize));
}
fontValue=!fontValue;
});
/*임시객체*/
buttonOK.setOnAction(new EventHandler<ActionEvent>() {
@Override
public void handle(ActionEvent event) {
if(fontValue) {
label.setText("HELLO");
label.setFont(new Font(30));
}
else {
label.setText("Hello, JavaFX");
label.setFont(new Font(fontSize));
}
fontValue=!fontValue;
}
});
/*함수식*/
buttonOK.setOnAction((event)-> {
handlerAction(event);
});
...
private void handlerAction(ActionEvent event) {
if(fontValue) {
label.setText("HELLO");
label.setFont(new Font(30));
}
else {
label.setText("Hello, JavaFX");
label.setFont(new Font(fontSize));
}
fontValue=!fontValue;
}
