사용하게 된 계기
혼자 진행중인 사이드 프로젝트가 있다. 회사에 대한 정보를 조회하는 간단한 프로젝트인데, 이슈를 생성하고 RP을 통해 깃 관리를 테스트해보고 싶은 마음에 만든 프로젝트다. 급한 마음에 이슈부터 호다닥 만들어 브랜치를 생성했는데, 아뿔싸! 프로젝트 기본 설정조차 제대로 만들지 않아서 main에서 변경이 일어났다.
1
2
3
A first-issue 😢
/
B---C---D---E---F main
이슈관리를 성급히 생각한 죄다 🔫 빵야
어떻게 하면 현재 main의 상태로 시작한 것처럼 할 수 있을까 하고 고민하고 있었는데, 인텔리제이에서 ‘리베이스’라는 기능을 발견했다. 💡
기존에 사용하던 merge와 rebase의 차이부터 알아보자
merge
Join two or more development histories together
둘 이상의 개발 이력을 함께 연결합니다.
rebase
Forward-port local commits to the updated upstream head.
업데이트된 업스트림 헤드에 대한 포트 로컬 커밋을 전달합니다.
정의만 봐서는 이해하기가 어렵다. 둘다 깃 이력에 관한 이야기를 하는 것이라 비슷해 보이기도 한다. 하나는 이력을 연결하는 것에 초점을 두고 있고, 하나는 헤드의 변경과 관련있어 보인다.
좀더 면밀히 살혀보자.

아래는 Git 문서에서 설명하는 Git Rebase 이다. series of. 연관된 사건들을 이야기 할 때 사용되는 것이다. (땡큐 말해보카)
About Git rebase
The
git rebasecommand allows you to easily change a series of commits, modifying the history of your repository. You can reorder, edit, or squash commits together.
git rebase명령을 사용하면 일련의 커밋을 쉽게 변경하여 저장소의 기록을 수정할 수 있습니다. 커밋을 함께 정렬하거나 편집하거나 스쿼시할 수 있습니다.
Warning
⚠️ Warning: Because changing your commit history can make things difficult for everyone else using the repository, it’s considered bad practice to rebase commits when you’ve already pushed to a repository. To learn how to safely rebase on GitHub.com, see “About pull request merges.”
경고: 커밋 기록을 변경하면 리포지토리를 사용하는 다른 모든 사람이 어려워질 수 있기 때문에 이미 리포지토리로 푸시했을 때 커밋을 다시 설정하는 것은 잘못된 관행으로 간주됩니다. GitHub.com 에서 안전하게 기본값을 다시 설정하는 방법은 “About pull request merges“를 참조하십시오

그렇지만 여전히 이해가 가지 않는다. 실습을 통해서 눈(손)으로 확안허는 방법도 있지만 공식문서를 좀더 보자.
예제를 통해서 알아보자
Merge

참고로 merge는 이것 하나로 설명이 완벽하고, 더 다른 예제는 없다.
Rebase

Rebase에 대한 예제는 상황별로 꽤나 다양하게 제공하고 있다. 꼭 한번 들어가서 직접 본다면 이해하는데 더 큰 도움이 되리라고 생각된다.
Rebase의 또다른 예제
이번 예제를 통해서 Rebase의 장점을 확실히 알 수 있다. 이 예제를 보면서 조금 더 깊이 이해를 해보자.
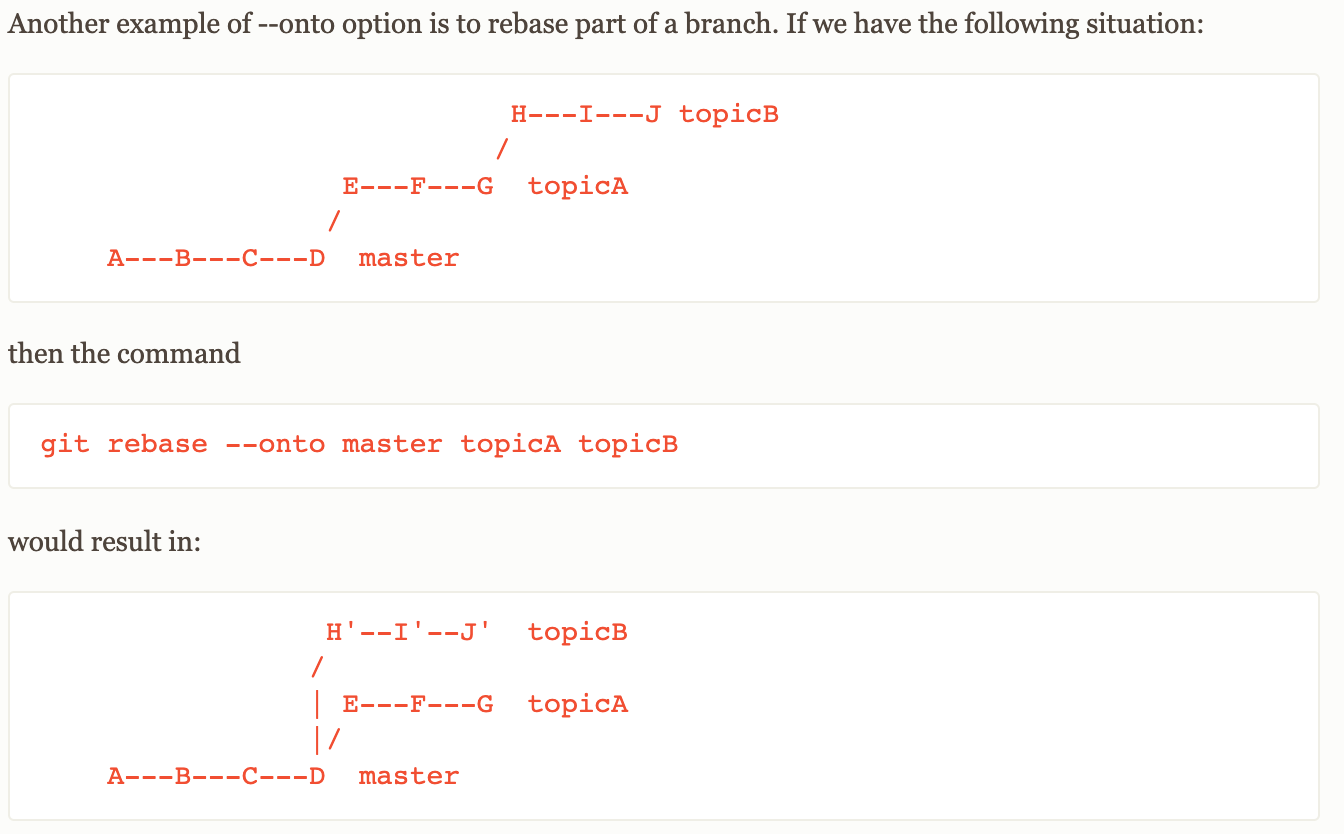
위의 예제에서 rebase 전 브런치들의 관계는 topicB가 topicA로부터 파생되어져 있었다.
1
master --> topicA --> topicB
하지만 이런 저런 이유로, A의 변경사항을 제외하고 master로부터 topicB가 시작이 되야하는 상황인 것이다. (topicA에 만들어진 기능이 쓸모없어졌다던가, 새로운 버전으로 업그레이드를 시도했는데 실패했다던가, 등등 슬픈 이유들이 대부분일 것 같다.)
1
2
master --> topicA
--> topicB
이처럼, merge 처럼 브랜치들을 합치는 용도(처럼보일 수 있지만 병합과는 의미가 조금 다르지만)로 사용할 수도 있고, 나눌 수도 있다(지만 역시 이것도 나누기보다는 어디서부터 시작할 것인가의 문제이다.)
아래는 깃 문서에서 설명하는 Rebase의 용도이다.
Typically, you would use git rebase to:
- Edit previous commit messages (이전 메시지 편집)
- Combine multiple commits into one (여러 커밋을 하나로 결합)
- Delete or revert commits that are no longer necessary (더 이상 필요하지 않은 커밋 삭제 또는 되돌리기)
그리고 다시 위의 Rebase 정의를 보자.
The
git rebasecommand allows you to easily change a series of commits, modifying the history of your repository. You can reorder, edit, or squash commits together.
git rebase명령을 사용하면 일련의 커밋을 쉽게 변경하여 저장소의 기록을 수정할 수 있습니다. 커밋을 함께 정렬하거나 편집하거나 스쿼시할 수 있습니다.
이제서야 일련의 커밋을 쉽게 변경할 수 있다는 말이 조금 이해된다.
그렇다면 팀에는 어떻게 규칙을 정하면 좋을까?
특히 프로세스에 익숙하지 않은 사용자의 경우 더 복잡하고 오류가 발생하기 쉬울 수도 있습니다. 다음은 리베이스 전략을 채택할 때 고려할 수 있는 몇 가지 지침과 규칙입니다.
👍 Do
- 기능 분기 활용: 특정 작업을 위해 기능 분기에서 작업하도록 권장
- 병합 전 리베이스: 선형 히스토리를 위해 기능 분기를 기본 분기로 리베이스
- 명확한 커뮤니케이션 설정: 브랜치가 리베이스된 시점에 대해 명확하게 커뮤니케이션 하기!
- 백업 만들기: 리베이스를 수행하기 전에 항상 백업 분기를 만들어두기
❌ Don’t
- 공유 브랜치 리베이스 방지: 여러 사람이 사용 중인 브랜치를 리베이스하지 마십시오.
- 대화형 리베이스를 신중하게 사용하십시오: 대화형 리베이스를 주의 없이 사용하지 마십시오. 불일치와 갈등을 일으킬 수 있음 ㅠ
권장사항
- 도구 및 자동화 고려: 리베이스 및 병합 프로세스를 단순화할 수 있는 도구를 활용
- 커밋 원자성 유지: 작고 독립적인 커밋을 권장
- 코드 검토 활용: 강력한 코드 검토 프로세스를 구현
- 작업 흐름 문서화: 일관성을 위해 전략을 잘 문서화 하기
GPT에게 물어보았다. 문제와 해결방법
Using a rebase strategy in Git can bring several benefits but can also introduce problems if not handled properly. Here are some common problems that might arise, along with possible solutions:
1. Problem: Conflicts with Shared Branches
- Cause: Rebasing a branch that others are working on leads to rewritten history, causing conflicts.
- Solution: Communicate clearly when a branch will be rebased and avoid rebasing branches that others are using. Stick to rebasing feature branches that are being used by a single developer.
2. Problem: Complex History with Interactive Rebase
- Cause: Using interactive rebase without care can lead to a confusing, tangled history.
- Solution: Use interactive rebase sparingly and provide proper training and guidelines to those who will use it.
3. Problem: Conflicts During Rebase
- Cause: Conflicts can occur when changes conflict with others in the target branch.
- Solution: Ensure that developers understand how to resolve conflicts during a rebase, possibly providing training or documentation. Encourage atomic commits to minimize conflicts.
4. Problem: Loss of Context with Squashed Commits
- Cause: Overly aggressive squashing of commits can lead to loss of context and history.
- Solution: Encourage developers to only squash closely related changes and to provide clear, descriptive commit messages to maintain context.
5. Problem: Lack of Understanding or Confusion
- Cause: Team members may be unfamiliar with rebase, leading to mistakes or avoidance of the feature.
- Solution: Provide education and support to ensure that everyone understands how and when to use rebase.
6. Problem: Accidental Overwriting of History
- Cause: A mistake during rebase can overwrite history, leading to loss of work.
- Solution: Always create backup branches before performing a rebase and consider using tools or automation to manage the rebase process.
7. Problem: Merging Commits from Other Branches
- Cause: Rebasing can cause commits from other branches to be replayed in an unwanted manner.
- Solution: Understand the proper target branch for the rebase and consider using
git pull --rebaseinstead ofgit pull, which will rebase only your changes instead of merging others.
8. Problem: Difficulty in Collaborating
- Cause: Constantly rebasing can make it difficult for team members to synchronize their work.
- Solution: Implement clear guidelines on when and where rebase should be used and maintain clear communication between team members.
The keys to successfully utilizing rebase are clear communication, proper education, and the establishment of guidelines that reflect the workflow and skills of your team. By understanding potential problems and implementing these solutions, you can make rebase a powerful part of your team’s development process.
결론
- Merge
- 작업: 두 분기의 내용을 결합하여 병합을 나타내는 새 커밋을 생성
- 히스토리: 병렬 개발 히스토리를 보존하면서 커밋의 연대순을 유지. 이로 인해 비선형의 분기된 기록이 생성될 수 있음..
- 협업: 기존 커밋 기록을 변경하지 않으므로 공유 브랜치에 적합
- 사용법: 종종 한 분기의 기능이나 수정 사항을 기본 또는 공유 분기로 결합하는 데 사용됨
- Rebase
- 작업: 한 가지에서 변경 사항을 가져와서 다른 가지 위에서 “재생”하여(replay) 효과적으로 가지를 이동하거나 결합함
- 히스토리: 한 브랜치에서 다른 브랜치로 직접 변경 사항을 배치하여 변경 사항이
다른 시점에 발생한 것처럼 보이도록 선형 히스토리를 생성 - 협업: 커밋 기록을 다시 작성하므로 공유 브랜치에 문제가 될 수 있음..
로컬,개별지점에서 가장 잘 사용! - 사용법: 종종 로컬 개별 분기를 기본 분기의 최신 코드로 업데이트하거나 병합하기 전에 기능 분기의 기록 정리에 사용
본질적으로 ‘merge’는 분기된 전체 변경 내역을 유지하는 반면 ‘rebase’는 보다 능률적이고 선형적인 Tree로 관리할 수 있다. 프로젝트의 필요에 따라 사용하겠지만… ‘rebase’는 히스토리 관리를 더 깨끗하고 이해하기 쉽게 만들 수 있지만 특히 협업 환경에서 신중하게 사용해야할 것 같다. 그래서 더 안전하게 쓰일 수 있는 ‘merge’를 통해 브런치 병합을 통해 깃 관리를 선호하는걸지도..?!
소수나 혼자 사용하는 브랜치에서는 적용하면 좋을 듯 하다. 꼭꼭 백업 브랜치 생성하고 Rebase 실행하기! :-)

